July 14, Police station – Montornès del Vallès
22-year-old. Shot: deceased
- Last update: 15:12 - First published
Unfortunately, we are witnessing a new episode of police and institutional racism. It is not an isolated incident in Montornès del Vallès, but is part of a machinery of persecution and criminalization of our migrant and racialized communities, throughout the Spanish territory, including in Catalonia.
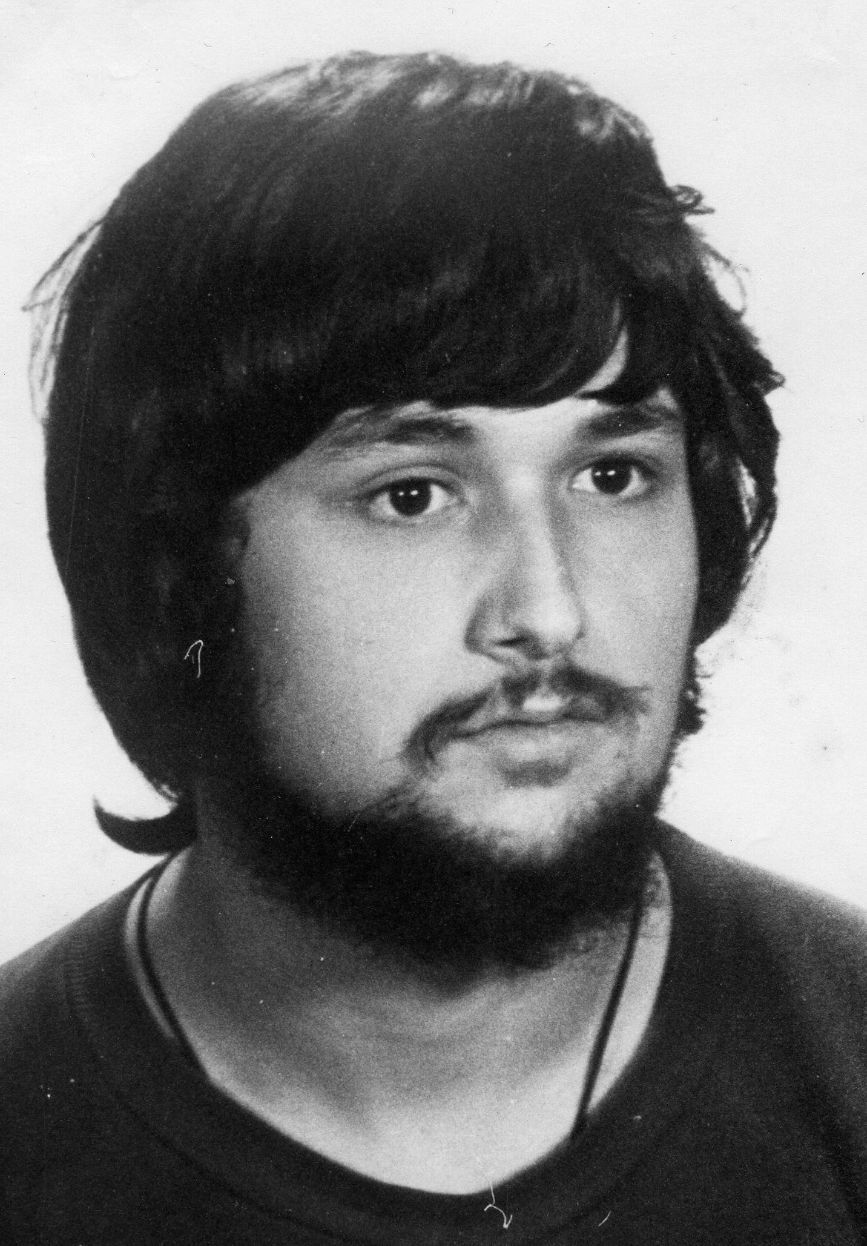
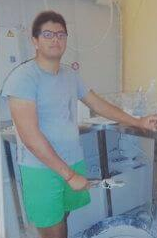
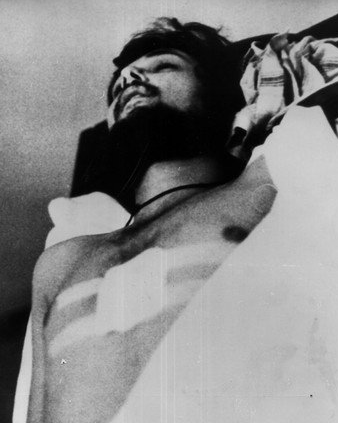
Mahamedi was a 22-year-old black man, a resident of Montornès del Vallès, born in Catalonia, son of Gambian parents. This lifelong villager —a former football player in the lower categories of the village team, who worked delivering packages to neighbors as a delivery man— died from gunshot wounds.
It happened last Friday, July 24, at the Local Police headquarters, under the opacity of all the administrations and media outlets that, in unison, rushed to establish a criminalizing narrative, when referring to our neighbor.
The Montornès del Vallès City Council, far from taking steps to inform the family of Mahamadi‘s death and clarify the facts, rushed to issue an institutional statement on social media. They talk about an “incident” at police stations, in which “an armed man” entered the police station, “was shot” by an officer, while “another officer was injured“. They omit to define how the latter was injured, and they do not even mention why a shot caused the death of a local resident. Nor did they communicate with the respect due to his family the violent death of Mahamedi.
We see once again how the media has finished constructing the official narrative, asserting that the young man was carrying a knife to a police station, and that it was an accident. This has given space to the police unions to request more personnel and resources to “prevent these regrettable events” of which police officers are victims, without any mention of the young man who lost his life in the police action.
We are once again faced with the death of a black person, with opacity in communication protocols and undignified treatment, in police stations, which refers us to other cases of police and institutional racism and deaths by gunfire from state security forces.
To clarify the regrettable facts and establish responsibility for the authorship of this death in police custody of the young Mahamedi, we ask:
- Clarification of the facts and why a firearm was used to reduce the victim. How many shots and in what area of the body were fired to cause the death of young Mahamedi?
- To know why the family was not informed of the death at the same time and why questions were asked at the victim’s home in the hours following his death?
- Mahamedi was a well-known neighbor and recognized among his community as a peaceful person. How can the use of firearms to kill and the fact that other forms of restraint were not used be justified?
- We ask the media for responsibility and journalistic rigor. That they do not serve as a hook to criminalize a person without having verified the facts beyond reproducing the police version that criminalizes and dehumanizes the young Mahamedi. Especially, in a context of growing threats and hate speech against Muslim and racialized migrant communities by far-right criminal organizations.
From several anti-racist social groups we demand that the cause of death at our neighbor’s police station be clarified. We demand dignified institutional treatment towards the family and responsibilities, to seek truth, justice and reparation regarding the death of young Mahamedi.
Physical violence
| Arrest | |
| Detention / Custody | |
| Hustle / Projection | |
| Prone position / lying flat on the stomach / ventral decubitus | |
| “Folding” (holding a person in a seated position with their head resting on their knees) | |
| Painful armlock | |
| Kicks, punches, slaps | |
| Feet / knees on the nape of the neck, chest or face | |
| Blows to the victim while under control and/or on the ground | |
| Blows to the ears | |
| Strangulation / chokehold | |
| Fingers forced backwards | |
| Spraying with water | |
| Dog bites | |
| Hair pulling | |
| Painful tightening of colson ties or handcuffs | |
| Painfully pulling by colson ties or handcuffs | |
| Sexual abuse | |
| Striking with a police vehicle | |
| Electric shocks | |
| Use of gloves | |
| X | Use of firearm |
| Use of “Bean bags” (a coton sack containing tiny lead bullets) | |
| Use of FlashBall weapon | |
| Use of sound grenade | |
| Use of dispersal grenade | |
| Use of teargas grenade | |
| Use of rubber bullets weapon (LBD40 type) | |
| Use of batons | |
| Use of Pepper Spray | |
| Use of Taser gun | |
| Use of tranquillisers | |
| Torture / Inhumane and degrading treatment | |
| Execution | |
| Kidnapping | |
| Disappearance |
Psychological violence
| Charge of disturbing public order | |
| Charge of rebellion | |
| Accusation of beatings to officer | |
| Charge of threatening officer | |
| Charge of insulting an officer | |
| Charge of disrespect | |
| Charge of resisting arrest | |
| Aggressive behaviour, disrespect, insults | |
| Intimidation, blackmail, threats | |
| Vexing or intimidating identity check | |
| Mock execution | |
| Intimidation or arrest of witnesses | |
| Prevented from taking photographs or from filming the scene | |
| Calls to end torment remained unheeded | |
| Prolonged uncomfortable position | |
| Failure to assist a person in danger | |
| Photographs, fingerprints, DNA | |
| Threat with a weapon | |
| Shooting in the back | |
| Charging without warning | |
| Kettling (corraling protestors to isolate them from the rest of the demonstration) | |
| Car chase | |
| Sexist remarks | |
| Homophobic remarks | |
| Racist comments | |
| Intervention in a private place | |
| X | At the police station |
| Mental health issues | |
| Harassment | |
| Body search | |
| Home search | |
| Violence by fellow police officers | |
| Passivity of police colleagues | |
| Lack or refusal of the police officer to identify him or herself | |
| Refusal to notify someone or to telephone | |
| Refusal to administer a breathalyzer | |
| Refusal to fasten the seatbelt during transport | |
| Refusal to file a complaint | |
| Refusal to allow medical care or medication | |
| Lies, cover-ups, disappearance of evidence | |
| Undress before witnesses of the opposite sex | |
| Bend down naked in front of witnesses | |
| Lack of surveillance or monitoring during detention | |
| Lack of signature in the Personal Effects Register during detention | |
| Deprivation during detention (water, food) | |
| Inappropriate sanitary conditions during detention (temperature, hygiene, light) | |
| Sleep deprivation | |
| Confiscation, deterioration, destruction of personal effects | |
| Pressure to sign documents | |
| Absence of a report | |
| Complacency of doctors |
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
- Lawyer :
- Collective :
- Donations :