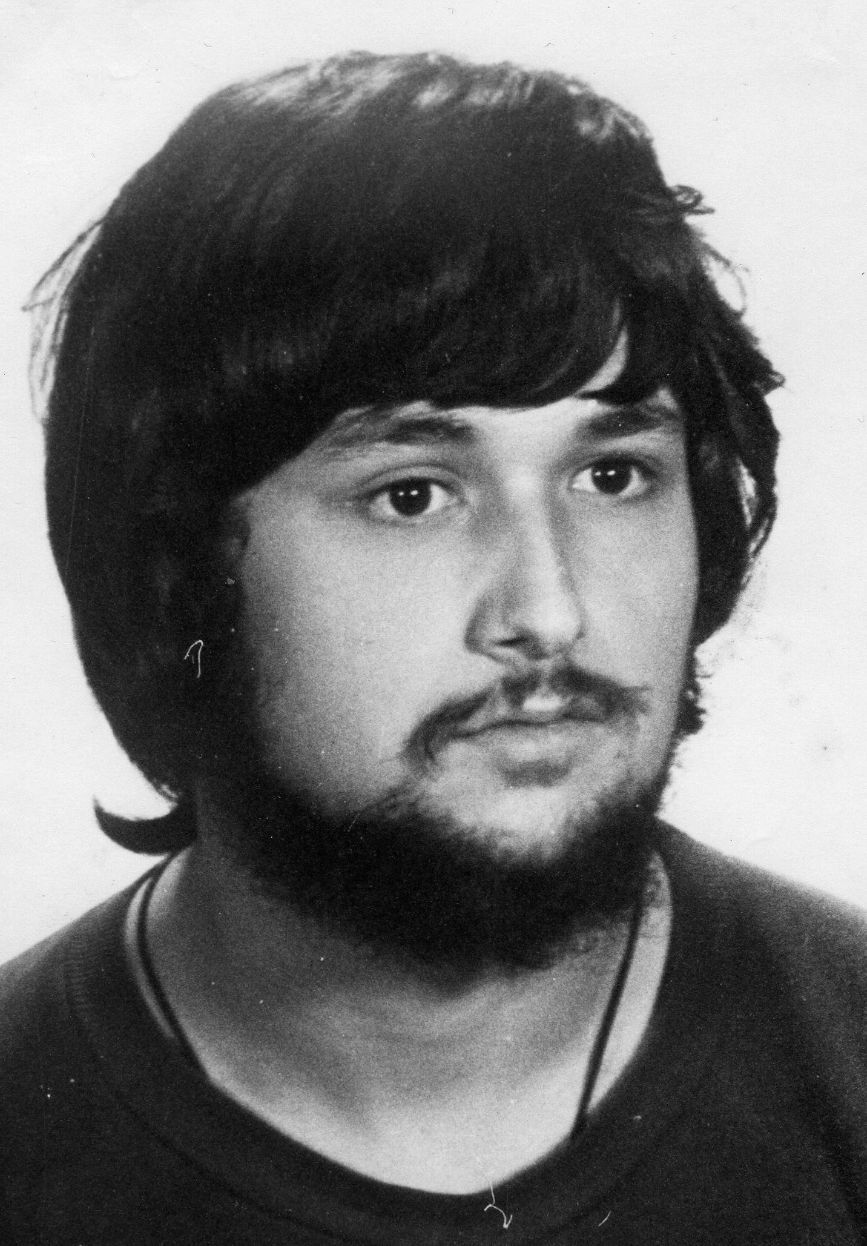
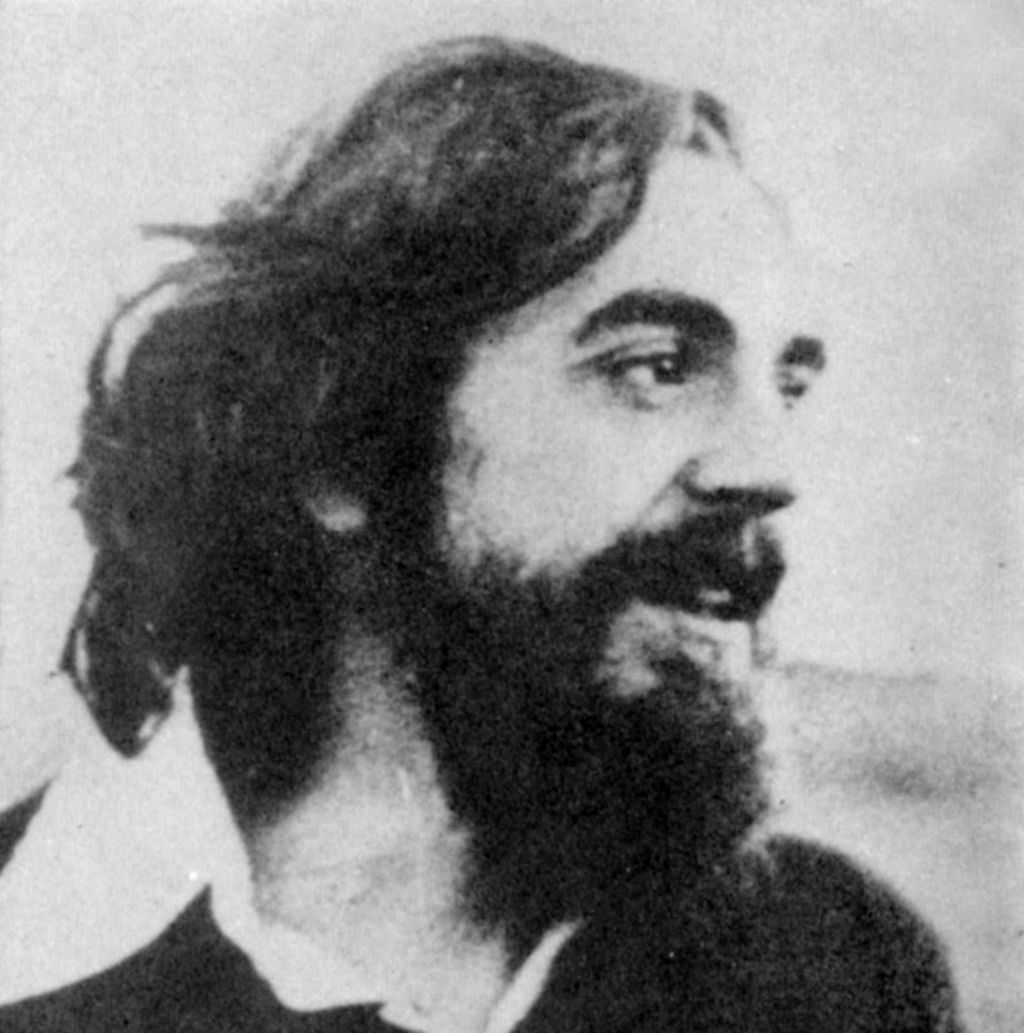
Franco Serantini was born in Cagliari in 1951 and was abandoned at birth at the city’s children’s home. When he was two years old he was entrusted to a Sicilian couple, but soon after his adoptive mother fell ill with cancer and died; the widower, left alone, was not allowed to finalize the adoption paperwork. When Franco was nine years old, he returned to the brefotrophy in Cagliari, where he remained until 1968, when the management of the institution informed the juvenile court that it was unable to follow the boy, who was not applying himself to his studies. The judge felt that the best solution to solve Franco‘s adolescent crisis was to lock him up in a reformatory, and so the boy was sent to the Men’s Re-education Institute in Pisa, “under a regime of semi-freedom,” meaning he had to eat and sleep in the institution.
In Pisa, however, Franco discovered political commitment, which, while on the one hand allowed him not to fall into the trap of common delinquency (which happens all too often in situations like his), on the other hand marked his death sentence. He was active in solidarity movements that organized low-cost markets, approached the anarchist movement, but also frequented the political milieu of Luciano Della Mea, a libertarian Marxist who represented for him the family he never had.
It is to Serantini‘s research that we owe the discovery of the well-known proclamation signed by Giorgio Almirante when he was chief of staff of the PS Office in Paganico (GR), in which he communicated
Pisa after 1968 was a city rich in political life. The “Pisan Workers’ Power” group (not to be confused with the Workers’ Power of Piperno, Negri and Scalzone) was founded in Pisa, which later gave birth to Lotta Continua, led (among others) by Luciano Della Mea and Adriano Sofri. In Pisa in those years the leaders of the communist youth were Massimo D’Alema and Fabio Mussi. Enrolled at the University of Pisa were many Greek anti-fascist students who were in exile because of the dictatorship of the colonels. Pisa was the scene of numerous clashes between fascists and police, between fascists and antifascists, and between antifascists and police, and it was at an antifascist demonstration that Franco Serantini, who had meanwhile become a militant anarchist, was beaten to death by police.
On May 5, the closing day of the election campaign, a rally was planned by the Missino deputy Giuseppe Niccolai, against whom Lotta Continua and the anarchists had called a protest demonstration.
Mayor Lazzari, taking into account the small size of the square and its location in the middle of narrow, winding streets, and fearing incidents (as had happened in previous days in other cities in Tuscany) asked the authorities together with the council and representatives of some parties (PCI, PSI and PSIUP) to move the rally to a less central area, but to no avail. On the other hand, 800 men of the I celere grouping, 500 carabinieri and 100 carabinieri paratroopers were rushed to the city to support the city’s PS units.
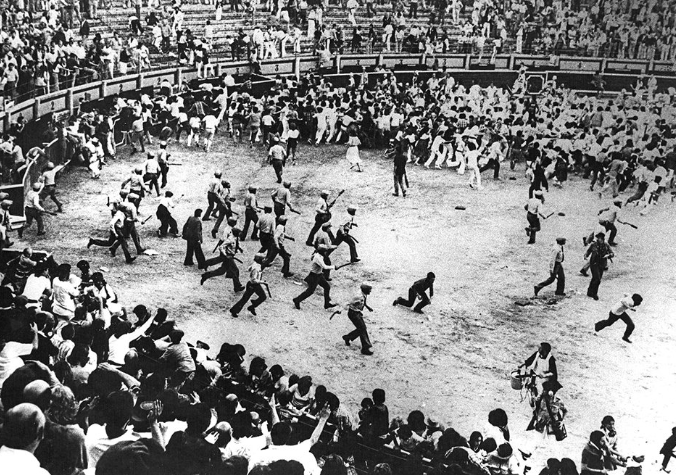
“The Missino deputy speaks in a square surrounded by shields, helmets, visor helmets, tromboncini with tear gas in the barrel, machine guns aimed. The fascists numbered perhaps two hundred, they shouted “Italy, Italy,” the deputy spoke for an hour and a half, a woman, Morena Morelli, came all the way under the stage, mocked the speaker, called him a fascist and was arrested.“
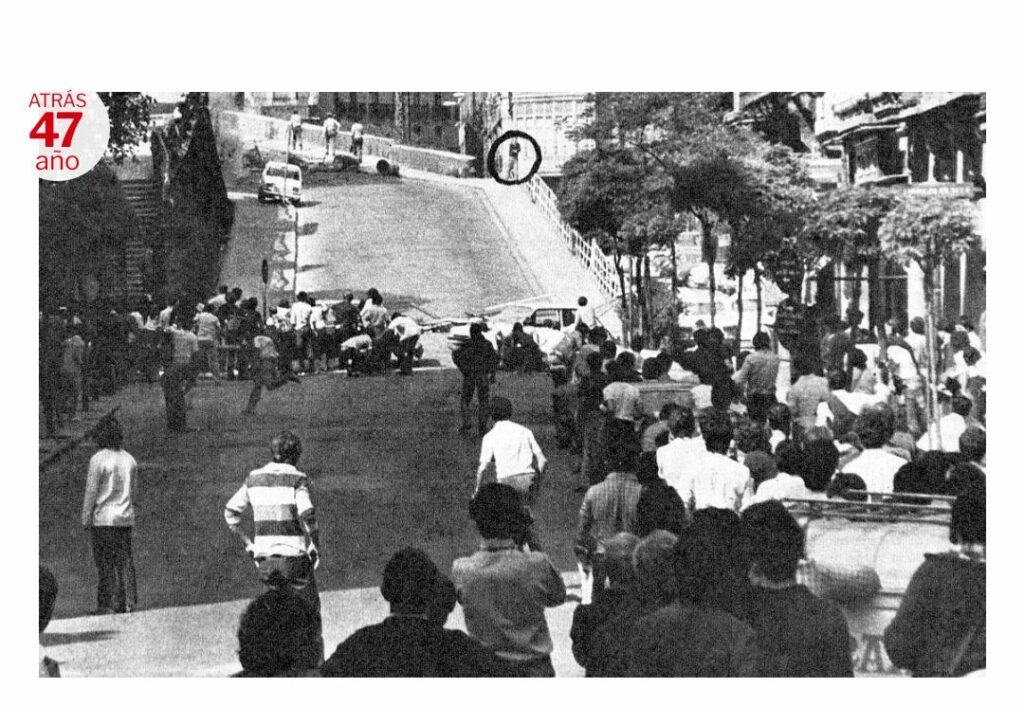
Around 6:30 p.m. police charges against the protesters began, and the historic center of Pisa experienced more than three hours of urban guerrilla warfare. The police threw tear gas not only on the protesters, but also inside the doorways of houses and even against the city hall.
“Mayor Lazzari looks out a window of the Gambacorti Palace and shouts at the policemen to stop targeting the municipality. “I said I was the mayor, that a council meeting was in progress (…) no one from above was threatening the police. They were pointing their guns up, firing one stick after another, giving the impression that they were drugged. It’s not as if they were listening to my words, they kept throwing sticks at the mullioned windows.’“
Dozens were beaten and battered protesters; some, hit by tear gas, had to be hospitalized. Some witnesses claimed to have seen police officers firing guns at eye level among the protesters.
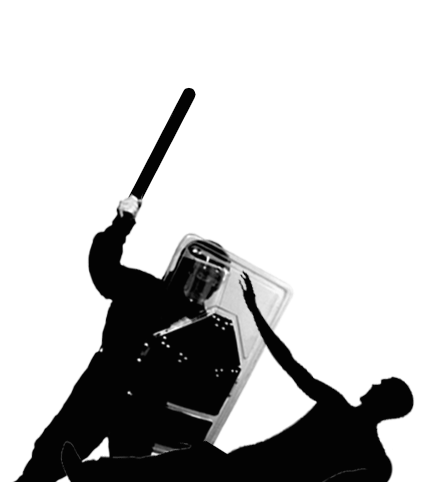
Franco Serantini was on the Lungarno Gambacorti, but inexplicably, instead of fleeing into the alleys, he lingered in the street. Thus recounted a resident of the Lungarno, Moreno Papini.
“… I saw that they were grabbing one (…) about fifteen celerini jumped on him and started beating him with incredible fury. They had circled over him so that he could no longer be seen, but you could tell from the gestures of the celerini that they had to hit him both with their hands and feet and with the kicks of their rifles. All of a sudden some of the celerini got out of the trucks there in front and intervened (…) “Enough, you’re going to kill him!” (…) one who looked like a graduate entered the middle and with another celerino they pulled him up. Only at that moment I could see his face, because he was holding his head dangling on his back….“
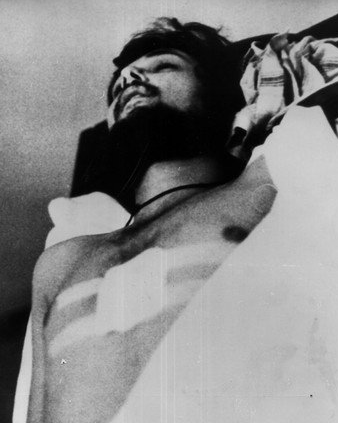
Franco was arrested and taken to the PS barracks. All those who saw him in the large room where the arrestees were put testified that it was clearly seen that he was very sick: he was unable to hold his head up, he could not speak, he had a yellowish color in his face. Nevertheless, no one thought of having him admitted to the hospital, or even of having him seen by a doctor; they took him to the jail, where he was interrogated by the magistrate on duty, who claimed to have asked for a medical examination for him, a detail that the public defender said he did not remember. Franco was examined only four hours after the interrogation, but the doctor merely prescribed an ice pack, did not measure his blood pressure, and did not have any X-rays taken. Taken back to his cell, his comrades became concerned as they saw him deteriorate but throughout the night on Saturday no one took any action. Only on Sunday morning was Franco taken to the prison emergency room, but by then it was too late: his heart stopped beating at 9:45 a.m. and the prison doctor wrote in the certificate “cerebral hemorrhage.”
The news of his death spread, and only because of the mobilization of friends and the stubbornness of the registrar’s clerk, who refused to sign the authorization to transport the body, because, since it was a violent death, authorization from the Public Prosecutor’s Office was necessary, Franco Serantini‘s murder would not be covered up. It is Luciano Della Mea who is the first to take action and contacts lawyer Bianca Guidetti Serra to make a complaint. The lawyer tracks down an old law of popular action “which allows any citizen to constitute himself as a civil party in protection of a person assisted by a charitable institution who is without parents or relatives” (remember that for the laws of the time Franco was a minor at the time of his death, having not yet turned 21). This will allow the investigation to begin.
he outcome of the necropsy examination is a frightening report. Thus stated lawyer Sorbi, who had attended the examination.
“It was a trauma to watch the autopsy, to see that boy I knew being dissected. A butchered body, chest, shoulders, head, arms. There was not even a small surface untouched. I had a long night of nightmares.“
But in the end the investigation will not lead to the punishment of any perpetrator. The policemen responsible for Franco‘s death could not be identified (they had helmets); none of those who did not have the boy examined would be prosecuted.
“In May 1972 Commissioner Giuseppe Pironomonte, who tried, by arresting him, to remove Serantini from the fury of the officers, resigned from the police force. (…) after the death of the young anarchist, he undergoes a profound crisis, realizes that that of the policeman, as it is done in Italy, is not the job for him, realizes that it is difficult to try to change the system from within, and abandons the PS.“
Finally, a brief mention of the figure of the then quaestor of Pisa, Dr. Mariano Perris: he had previously served as an executive of the political squad in Milan and Turin, and his name was found, during a search in the offices of FIAT on 5/8/71, ordered by Praetor Guariniello, among those of the PS executives who allegedly collected bribes from FIAT for controlling the political activity of the company’s employees (on this see the publication edited by Lotta Continua in 1972, Agnelli is afraid and pays off the police headquarters).
After Pisa, Perris was appointed quaestor in Milan; but we must remember that during the period of the Germanic occupation of Trieste he had been one of the leaders (he was in charge of the “judicial squad”) of the Special Inspectorate of PS, better known in the city as the “Collotti gang,” a collaborationist body that distinguished itself by the ferocity with which its members conducted anti-partisan repression. Perris’s squad was in charge of arresting common criminals to be blackmailed or intimidated (during the trial of the “gang,” a witness asserted that the torture apparatus with electricity “also passed through Perris’s office”) in order to infiltrate them into the partisan movement or to be used directly in roundup operations.
Perris avoided being tried for collaborationism along with the other corps leaders by availing himself of an affidavit provided by the Triestine CLN (of nationalist and anti-communist persuasion): a witness asserted that his team did not deal with political issues (and its role was not investigated in depth), so that the commissioner continued his career in the PS of the “republic born of the Resistance,” with the resume we have seen.